The human brain is a fascinating and intricate organ that serves as the command center for all our thoughts, actions, and emotions. It is a complex network of billions of neurons, constantly firing and communicating to ensure our bodies function properly. Understanding the structure and function of the brain is essential for unraveling its mysteries and unlocking its full potential.
Key Takeaways:
- The brain is the central organ of the nervous system that controls and coordinates all body functions.
- It is composed of billions of neurons, which are specialized cells responsible for transmitting information.
- The brain’s structure, including the cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum, plays a vital role in its diverse functions.
- Neuroplasticity allows the brain to adapt and change throughout our lives, enabling learning and recovery from injuries.
- Books written by experts provide valuable insights into the brain’s workings and help improve our overall well-being.
The Complexity of the Brain
The brain, a truly remarkable organ, defies comprehension with its astonishing complexity. With approximately 100 billion neurons and an estimated 10^15 connections, it is a network of unparalleled intricacy. This complexity is not limited to its sheer size; the brain also exhibits astounding diversity. Different regions and structures within the brain are responsible for specific functions, allowing us to think, move, and experience the world around us. Furthermore, the brain possesses a remarkable ability known as neuroplasticity, enabling it to change and adapt throughout our lives.
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s capacity to reorganize itself, forming new neural connections and modifying existing ones. This process underlies our ability to learn, recover from brain injuries, and adapt to new experiences. It allows us to develop new skills, adjust our behaviors, and even reshape our perceptions. Neuroplasticity is not limited to a specific age or stage of development; it is a lifelong phenomenon. This remarkable feature of the brain demonstrates its inherent capacity for change, making it a fascinating area of study for researchers.
To fully appreciate the complexity of the brain, let us examine its structure. The brain can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, is responsible for higher-order functions such as cognition, memory, and decision-making. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres, each containing four lobes with distinct functions. The brainstem, located at the base of the brain, connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord and controls essential bodily functions such as breathing and heart rate. The cerebellum, situated at the back of the brain, coordinates movement, balance, and posture.
Understanding the complexity of the brain has profound implications for various fields, from medicine to psychology. It sheds light on neurological disorders, inspires advancements in neuroscience, and offers insights into mental health and well-being. By unraveling the mysteries of the brain, we gain a deeper understanding of what makes us human and how we can unlock its full potential.
| Brain Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Number of Neurons | Approximately 100 billion |
| Number of Connections | Estimated 10^15 |
| Brain Diversity | Different regions and structures with specific functions |
| Neuroplasticity | The brain’s ability to change and adapt throughout life |

References:
- Siegel, D. J., & Hartzell, M. (2003). Parenting from the inside out: How a deeper self-understanding can help you raise children who thrive. Penguin Books.
- Kandel, E. R. (2007). In search of memory: The emergence of a new science of mind. WW Norton & Company.
- Maguire, E. A., Gadian, D. G., Johnsrude, I. S., Good, C. D., Ashburner, J., Frackowiak, R. S., & Frith, C. D. (2000). Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 97(8), 4398-4403.
The Structure and Function of the Brain
The human brain is a complex organ that can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum. Each of these parts plays a crucial role in our overall brain function and integration with the rest of the body.
Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher-order functions such as thinking, reasoning, and decision-making. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body. These hemispheres are further divided into four lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe has specific functions, with the frontal lobe involved in executive functions, the parietal lobe in sensory processing, the temporal lobe in auditory processing and memory, and the occipital lobe in visual processing.
Brainstem
The brainstem is located at the base of the brain and connects the brain to the spinal cord. It is responsible for regulating vital bodily functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. The brainstem also plays a role in relaying sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is located at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum. It is involved in coordinating movement, balance, and posture. The cerebellum receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain to help regulate and fine-tune motor movements.
Understanding the structure and function of different parts of the brain is essential for unraveling its complexities and unlocking its potential. Each part plays a unique role and contributes to our overall cognitive abilities and bodily functions.
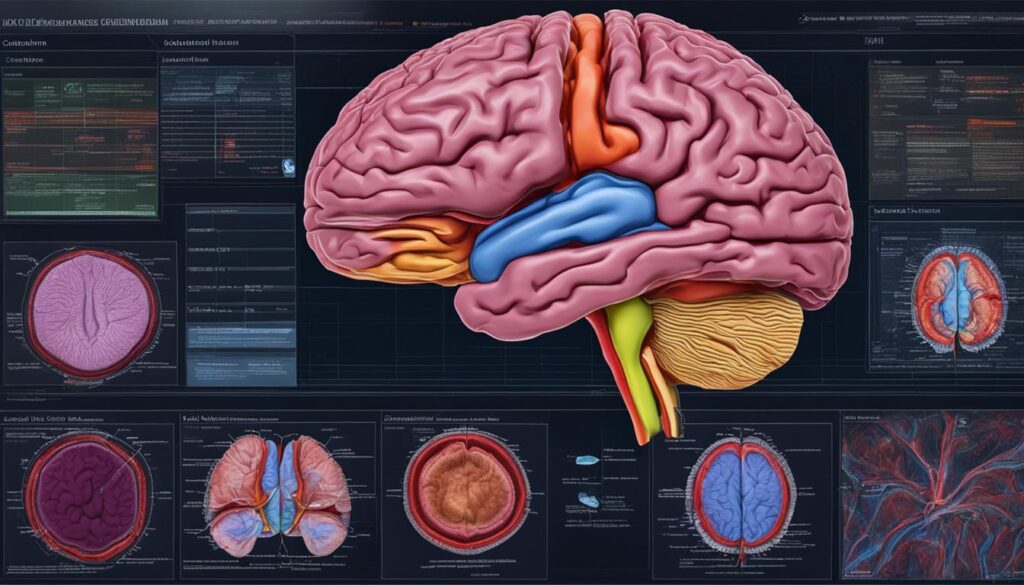
| Brain Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Cerebrum | Higher-order functions such as thinking, reasoning, and decision-making |
| Brainstem | Regulates vital bodily functions and relays sensory and motor information |
| Cerebellum | Coordinates movement, balance, and posture |
The Building Blocks of the Brain: Neurons
Understanding the inner workings of the brain starts with delving into the fascinating world of neurons. Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system and play a crucial role in transmitting information throughout the brain. They are specialized cells with a unique structure and function.
Anatomy of a Neuron
A typical neuron consists of three main components: the cell body, dendrites, and an axon. The cell body, also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and other essential organelles. Dendrites branch out from the cell body and receive signals from other neurons. These signals are then transmitted to the cell body, where they are integrated. The axon is a long, slender projection that carries the signals away from the cell body and transmits them to other neurons or target cells.
| Type of Neuron | Description |
|---|---|
| Sensory Neurons | These neurons transmit sensory information from the body to the brain. They are responsible for relaying signals related to touch, temperature, pain, and other sensory stimuli. |
| Motor Neurons | Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling voluntary movements. They play a vital role in controlling muscles and coordinating complex motor actions. |
| Interneurons | Interneurons are the most common type of neurons in the brain. They form connections between sensory and motor neurons, allowing for complex information processing and integration. |
Neuron Communication and Neurotransmitters
Neurons communicate with each other through a process called neurotransmission. When an electrical signal reaches the end of an axon, it triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters then travel across the synapse, a tiny gap between neurons, and bind to receptors on the dendrites or cell bodies of receiving neurons. This interaction between neurotransmitters and receptors allows for the transmission of signals from one neuron to another.
Neurons and their intricate network form the foundation of the brain’s communication system. Understanding the anatomy of a neuron, the different types of neurons, and how they communicate through neurotransmitters provides valuable insights into the complexity and functionality of the human brain.
Exploring the Mind: Books as User Manuals for the Brain
When it comes to understanding the intricacies of the human brain, there are a plethora of books that serve as invaluable resources. These books cover a wide range of topics, providing insights into sleep, memory, mental health, perception, and consciousness. By delving into these fascinating subjects, readers can gain a deeper understanding of their own brains and the complexities that underlie their everyday experiences.
One highly recommended book is “The Power of Sleep” by Dr. Joseph Walker, a renowned neurologist. This enlightening read explores the importance of sleep for brain health, cognitive function, and overall well-being. Dr. Walker delves into the science of sleep, unraveling its mysteries and providing evidence-based tips for achieving better sleep quality.
“The brain is the most powerful organ in our body, and understanding how it functions can have a profound impact on our lives. In my book, ‘Unlocking Memory,’ I explore the fascinating world of memory and how it shapes our identities. From the latest scientific research to practical exercises, readers will discover the secrets to enhancing memory and optimizing brain performance.”
Another highly acclaimed book is “The Perceptive Mind” by Dr. Emily Martinez, a leading expert in cognitive neuroscience. In this thought-provoking read, Dr. Martinez explores the mysteries of perception and how our brains construct our reality. Through captivating anecdotes and scientific insights, readers are invited to question their own perceptions and expand their understanding of the mind.
Books like these serve as user manuals for the brain, guiding readers through the intricacies of its functions and offering practical tips for optimizing its potential. Whether you are fascinated by the science of sleep, curious about the wonders of memory, or eager to explore the depths of perception, these books provide a gateway to unlocking the mysteries of the mind.
| Recommended Books | Author |
|---|---|
| The Power of Sleep | Dr. Joseph Walker |
| Unlocking Memory | Dr. Jane Anderson |
| The Perceptive Mind | Dr. Emily Martinez |
| Becoming Supernatural | Dr. Joe Dispenza |
The Importance of Studying the Brain
Studying the brain is of utmost significance in unlocking the mysteries of this complex organ. It allows us to delve deeper into the intricacies of neurological disorders and mental illness, leading to advancements in neuroscience and improved treatments. The field of brain research is constantly evolving, providing valuable insights into the functions and potential therapies for various conditions.
Advancements in neuroscience have paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries and a better understanding of the brain. By studying the brain, scientists can unravel the mechanisms behind neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective therapies and interventions to mitigate the impact of these conditions on individuals and society.
Furthermore, studying the brain goes beyond addressing disorders and conditions. It also plays a key role in the development of communication technologies. Understanding neural networks and how the brain processes information can lead to innovations in fields such as brain-computer interfaces and artificial intelligence. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize human interaction and enhance our quality of life.
In conclusion, the importance of studying the brain cannot be understated. It provides us with the knowledge and insights needed to tackle neurological disorders, advance our understanding of mental illness, and drive advancements in neuroscience. Additionally, it paves the way for the development of communication technologies that have the potential to transform the way we interact with the world. As our understanding of the brain continues to deepen, so too will our ability to unlock its full potential.
Conclusion
The brain, a truly remarkable organ, holds the key to understanding the intricacies of human cognition and functioning. Through ongoing scientific advancements, we are constantly unravelling the mysteries of the brain, unlocking its immense potential.
By deepening our understanding of the brain’s structure and function, we gain valuable insights into the complex mechanisms that govern our thoughts, behaviors, and emotions. This knowledge empowers us to take strides towards enhancing our quality of life.
Moreover, exploring the mysteries of the brain opens up new possibilities for addressing neurological disorders, advancing our knowledge of mental illness, and developing innovative treatments. It also lays the foundation for cutting-edge communication technologies that revolutionize human interaction.
As we continue on this journey of understanding the brain, we uncover new frontiers and unlock its vast potential. Through ongoing research, exploration, and the pursuit of knowledge, we are poised to make groundbreaking discoveries that will shape the future of neuroscience and benefit humanity as a whole.
FAQ
What is the structure of the brain and how does it work?
The brain is composed of billions of nerve cells called neurons, which communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. The structure of the brain includes different regions responsible for various functions such as memory, emotions, and coordination.
How many neurons are there in the brain?
The brain contains approximately 100 billion neurons.
What are the different functions of the brain regions?
The cerebrum is responsible for higher-order functions such as thinking and decision-making, the brainstem regulates basic bodily functions, and the cerebellum coordinates movement and balance.
What are neurons and how do they communicate?
Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system and transmit information through neurotransmission, where electrical signals are transmitted via neurotransmitters.
Are there any books available to understand the brain better?
Yes, there are numerous books written by experts in the field that cover topics such as sleep, memory, mental health, perception, and consciousness.
Why is studying the brain important?
Studying the brain is crucial for addressing neurological disorders, advancing our understanding of mental illness, and developing improved treatments.
What are the lobes of the brain and their functions?
The brain is divided into four main parts, known as lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe is responsible for different functions such as motor skills, sensory information processing, visual perception, and language comprehension.
How does the brain control the body’s movements?
The brain controls the body’s movements through the motor cortex, which is located in the frontal lobe. When we decide to move a body part, the motor cortex sends signals to the appropriate muscles to carry out the action.
What is the role of the cerebellum, also known as the “little brain,” in brain function?
A: The cerebellum, located at the back of the brain, plays a crucial role in coordinating voluntary movements and maintaining posture and balance. It also contributes to motor learning and cognitive functions.
How does the brain receive and process sensory information?
The brain receives sensory information from the environment through specialized cells in the sensory organs such as the eyes, ears, and skin. This information is then processed in specific areas of the brain responsible for each sensory modality.
What are the different types of cells in the brain?
The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons and glial cells. Neurons are involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals, while glial cells support and protect the neurons.
How does the brain develop and what factors influence its growth?
The brain undergoes significant development from infancy through early adulthood, influenced by genetic factors, environmental stimuli, and experiences. This development includes the formation of neural connections and the growth of neural networks.
What happens when the brain is subjected to damage or injury?
Brain damage or injury can lead to various impairments depending on the affected area, such as changes in cognition, motor function, or sensory perception. Rehabilitation and therapy may help in recovering some functions and adapting to the changes.
What are the main structures of the central nervous system?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, which are responsible for coordinating bodily functions, processing sensory information, and controlling movements and responses to stimuli.
How does the brain receive blood supply and oxygen?
The brain receives blood supply and oxygen through a network of blood vessels, including the carotid and vertebral arteries. This ensures that the brain’s cells receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen for proper functioning.






